Traffic Violation Modeling Using K-Means Clustering Method: A Case Study in Bandung, Indonesia
Main Article Content
Abstract
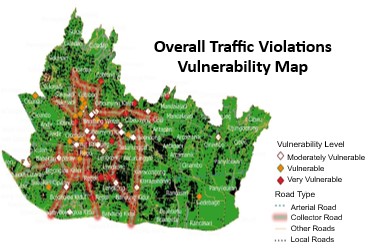
Violations of traffic regulations are both an issue and a problem that persists as a feature of life, especially in metropolitan regions such as Bandung. Traffic violation has both behavioral and environmental patterns, with different types of violations occurring at different times during the day. This negligence stems largely from not properly equipping the vehicle with the necessary documents, especially for drivers who do not pay attention to proper document preparation. With the goal of increasing road safety, law enforcement bodies face the ongoing challenge of managing rising traffic violation rates which results in a growing backlog of violation cases and a corresponding backlog workload for police departments. Comprehensive preventive strategies for the problem are extremely difficult to implement in the absence of streamlined mechanisms for the efficient allocation of limited police resources. Currently, agencies responsible for managing violation records are still using a manual desktop system based on Microsoft Excel spreadsheets. This method impedes the analysis of large datasets to derive actionable insights that could inform targeted, data-driven strategies needed to guide proactive measures. In this regard, this study attempts to implement the K-Means clustering technique in order to identify and classify high-incidence traffic violation areas in Bandung. Using this technique, the research classifies the city into three violation risk clusters: very prone, prone, and moderately prone areas. The map of the classes demonstrates the distribution of these clusters spatially, illustrating clearly and vividly how stakeholders can visualise the pattern of traffic violations. This method improves the understanding of data and at the same time boosts purposeful planning for the safety and public traffic order anticipations.
Article Details
References
[1] Sirwan K Ahmed, Mona G Mohammed, Salar O Abdulqadir, Rabab G Abd El-Kader, Nahed A El-Shall, Deepak Chandran, Mohammad E Ur Rehman, and Kuldeep Dhama. Road traffic accidental injuries and deaths: A neglected global health issue. Health Science Reports, 6(5):e1240, 2023.
[2] World Health Organization. Global status report on road safety 2023: summary. World Health Organization, 2023.
[3] Yibeltal Assefa Atalay, Bersufekad Wubie Alemie, Belete Gelaw, and Kelemu Abebe Gelaw. Epidemiology of road traffic accidents and its associated factors among public transportation in Africa: systematic review and meta-analysis. Frontiers in Public Health, 13:1511715, 2025.
[4] Intan Zainafree, Nadia Syukria, Silfia Addina, and Muhamad Zakki Saefurrohim. Risk factors of road traffic accidents in rural and urban areas of Indonesia based on the national survey of year 2018. Nigerian Postgraduate Medical Journal, 29(2):82–88, 2022.
[5] Bewket Tadesse Tiruneh, Berhanu Boru Bifftu, and Berihun Assefa Dachew. Prevalence and factors associated with road traffic incident among adolescents and children in the hospitals of Amhara National Regional State, Ethiopia. BMC Emergency Medicine, 19:1–6, 2019.
[6] Sarun Jongrak. Food delivery rider is not worker: The distortion of the Thai legal system. CMU Journal of Law and Social Sciences, 14(2):38–58, 2021.
[7] Siriaran Kwangsukstith, Vithawat Surawattanasakul, Chollada Mahakkanukrauh, Jinjuta Panumasvivat, Wachiranun Sirikul, Amornphat Kitro, and Penprapa Siviroj. Major injuries and associated factors in traffic accidents among motorcycle food delivery riders during the COVID-19 pandemic in Thailand. Heliyon, 10(20), 2024.
[8] Omar Elfahim, Marouane El Midaoui, Mohamed Youssfi, Omar Bouattane, et al. Traffic violations analysis: Identifying risky areas and common violations. Heliyon, 9(9):e19058, 2023.
[9] Jianyu Wang, Shuo Ma, Pengpeng Jiao, Lanxin Ji, Xu Sun, and Huapu Lu. Analyzing the risk factors of traffic accident severity using a combination of random forest and association rules. Applied Sciences, 13(14):8559, 2023.
[10] Sutanto Soehodho. Public transportation development and traffic accident prevention in Indonesia. IATSS Research, 40(2):76–80, 2017.
[11] Dwi Prasetyanto, Muhammad Rizki, and Andrean Maulana. The role of attitude, behavior, and road conditions in traffic violation among workers and students in Bandung City, Indonesia. The Open Transportation Journal, 17:2667–1212, 2023.
[12] Han Jiawei, Kamber Micheline, and Pei Jian. Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques.-3rd. Morgan Kaufmann, 2012.
[13] S Nagendra Babu and J Jebamalar Tamilselvi. A data mining framework to analyze road accident data using map reduce methods CCMF and TCAMP algorithms. International Journal of Simulation–Systems, Science & Technology, 19(5):p1–7, 2018.
[14] Sachin Kumar and Durga Toshniwal. A data mining framework to analyze road accident data. Journal of Big Data, 2:1–18, 2015.
[15] Salvador García, Julián Luengo, Francisco Herrera, et al. Data preprocessing in data mining, volume 72. Springer, 2015.
[16] Asroni Asroni and Ronald Adrian. Penerapan metode k-means untuk clustering mahasiswa berdasarkan nilai akademik dengan Weka interface studi kasus pada jurusan teknik informatika UMM Magelang. Semesta Teknika, 18(1):76–82, 2015 (in Indonesia).
[17] Mohiuddin Ahmed, Raihan Seraj, and Syed Mohammed Shamsul Islam. The k-means algorithm: A comprehensive survey and performance evaluation. Electronics, 9(8):1295, 2020.
[18] Wenbin Wu and Mugen Peng. A data mining approach combining k-means clustering with bagging neural network for short-term wind power forecasting. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 4(4):979–986, 2017.
[19] Emi Sukiyah and Nur Khoirullah. The Bandung City spatial planning policies in geological perspective. Journal of Geological Sciences and Applied Geology, 4(1):48–54, 2020.
[20] Nurpilihan Bafdal, Kharista Amaru, and Boy Macklin Pareira. Buku Ajar Sistem Informasi Geografis. Teknik Manajemen Industri Pertanian; Universitas Padjajaran, 2011.
[21] MA Khafid, AP Wicaksono, DR Saputra, FW Andita, and DS Wibowo. Geospatial modeling analysis of potential inundation impact of sea level rise: A case study of South Coast Yogyakarta. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, volume 830, page 032075. IOP Publishing, 2020.